What is Reasoning in AI? A Complete Guide
Published: 28 Sep 2025
What is reasoning in AI? In simple terms, it describes how machines reason, make decisions, and solve problems. Reasoning in artificial intelligence leverages the ability to connect facts, apply rules, and draw conclusions.
Similar to humans, AI uses reasoning to go from specific observations to general conclusions. This ability enables discovery or prediction and decision making in dynamic environments.
The various types or forms of reasoning — such as logical reasoning, monotonic reasoning, forward reasoning, backward reasoning — provide machines with the different flexibility in how they reason about knowledge and conclude.
From the expert systems in healthcare to autonomous vehicles driving on the road and large language models (LLMs) in our daily lives, reasoning is the source of power for real-world AI applications.
In this guide, we will cover an understanding of reasoning in AI; types of reasoning; examples of the combined types of reasoning; and challenges and future issues of reasoning in AI.
Table of Contents
What is Reasoning in AI?
Reasoning in AI is the process of making logical inferences. It allows machines to move from specific observations to general conclusions.
AI systems use a knowledge base (facts, rules, and data) along with an inference engine (the decision-making component). Together, they help machines predict outcomes and take action in dynamic environments.
In simple words: reasoning enables AI to think before it acts.
Types of Reasoning in AI
Logical Reasoning in AI
Logical reasoning uses structured rules. If the premises are true, the conclusion must also be true.
For example, in an expert system:
- Rule: “If fever and cough → then flu.”
- Input: “Fever and cough present.”
- Output: “AI concludes flu.”
This reasoning style is precise, reliable, and easy to explain. It is widely used in healthcare, law, and troubleshooting systems.
Monotonic Reasoning in AI
Monotonic reasoning means that once a conclusion is made, adding new information will not change it.
Example:
- Rule: “If all birds can fly → then a sparrow can fly.”
- Even if we later add new facts about penguins, the sparrow’s conclusion stays true.
This approach is consistent but struggles with real-world, dynamic environments, where new facts often change earlier decisions.
Forward Reasoning (Forward Chaining) in AI
Forward reasoning starts with known facts and applies rules to reach a conclusion.
Think of it as data-driven. AI begins with inputs and moves step by step until it finds an answer.
Example: medical diagnosis systems. The AI checks symptoms one by one until it arrives at the most likely disease.
Backward Reasoning (Backward Chaining) in AI
Backward reasoning works in the opposite way. It starts with a goal and works backward to check if the facts support it.
Think of it as goal-driven.
Example: troubleshooting a computer. The AI starts with “The system won’t start” and traces back to check possible causes like power failure, faulty hardware, or corrupted files.
Forward vs. Backward Reasoning
| Feature | Forward Reasoning | Backward Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Data-driven | Goal-driven |
| Used in | Diagnosis, monitoring | Troubleshooting, planning |
| Example | Healthcare system | Expert system debugging |
Both methods are vital. Choosing depends on the problem at hand.
Applications of Reasoning in AI
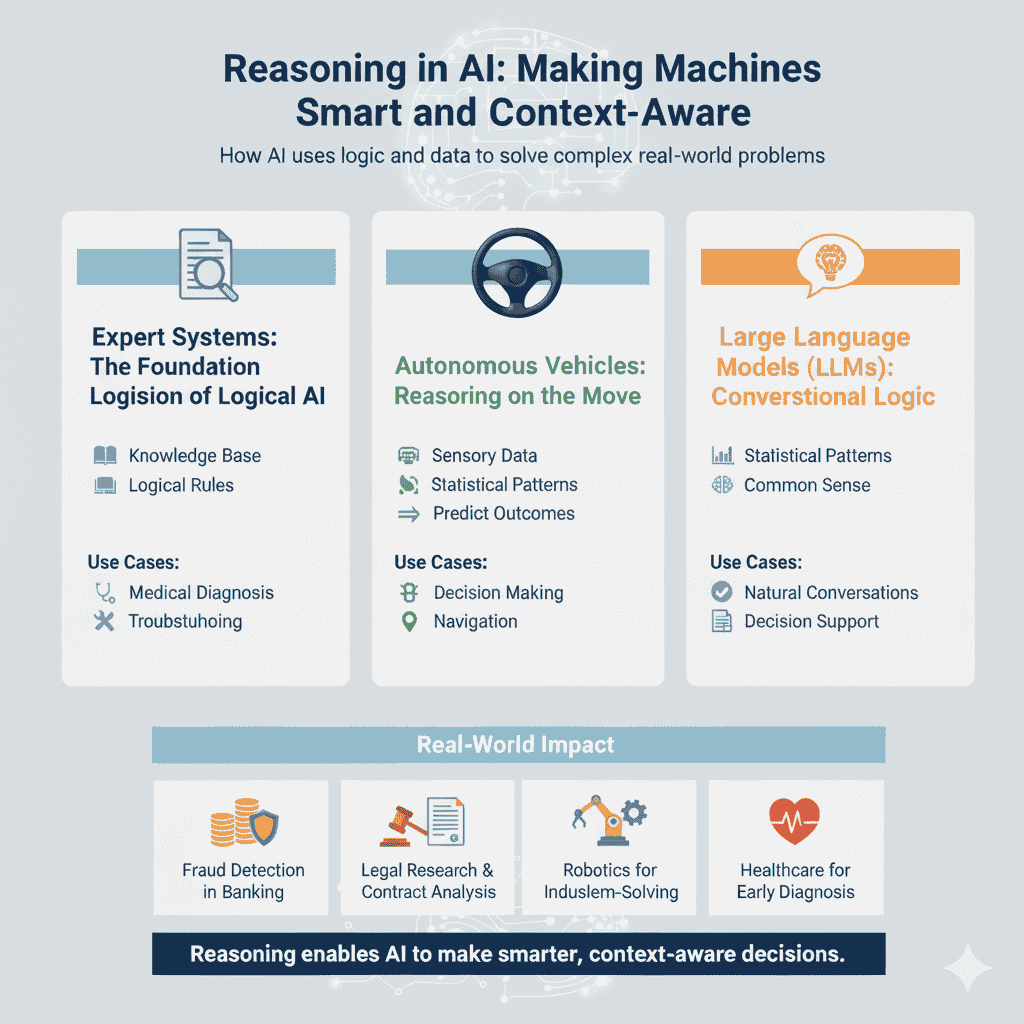
Expert Systems
Expert systems are early examples of AI reasoning. They mimic human experts by using a knowledge base and logical rules. Doctors use them for diagnosis, and engineers for troubleshooting.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on reasoning every second. They use sensory data to predict outcomes, such as when to stop, turn, or accelerate.
Reasoning helps them navigate dynamic environments where the situation changes constantly.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Modern AI, like ChatGPT, relies on reasoning to generate human-like responses. It blends statistical patterns with logical steps to deliver common sense answers.
This makes reasoning critical for natural conversations, decision support, and predictive outcomes.
Real-World Use Cases
- Fraud detection in banking
- Legal research and contract analysis
- Robotics for industrial problem-solving
- Healthcare for early diagnosis
Reasoning enables AI to make smarter, context-aware decisions.
Challenges in AI Reasoning
Reasoning is powerful, but it faces real challenges:
- Dynamic environments: New data can overturn old conclusions.
- Incomplete knowledge bases: AI may miss critical facts.
- Computational cost: Complex reasoning requires heavy resources.
Overcoming these limits is key to building reliable AI systems.
Future of Reasoning in AI

The future lies in combining symbolic reasoning with machine learning. Large language models are already moving in this direction.
Hybrid systems will handle both logic and context, enabling smarter decision-making processes.
From healthcare to autonomous vehicles, reasoning will continue to evolve. The goal is clear: bring AI closer to human-like common sense.
Conclusion
Reasoning is what elevates artificial intelligence beyond pattern recognition. Reasoning enables machines to use logic, draw assumptions, and solve problems in the real world.
Through a number of types of reasoning in AI—logical reasoning, monotonic reasoning, forward reasoning, and backward reasoning—systems can estimate future states and make informed decisions. These systems of reasoning drive applications in expert systems, self-driving vehicles, and large language models (LLMs).
There are still challenges to overcome, such as operating under incomplete knowledge and adapting to change in dynamic environments, but new models are being developed. Likely, future models will incorporate logic and reasoning into learning, leading to AI systems that are more intelligent and reliable.
In essence, reasoning is not just a function of AI—it is the primary capability that warrants the term, intelligence.
FAQs
What is non-monotonic reasoning in AI?
Non-monotonic reasoning allows AI to change conclusions when new information becomes available, making it useful for uncertain or evolving situations.
How does common sense reasoning work in AI?
Common sense reasoning helps AI understand everyday knowledge and context, allowing it to make practical decisions similar to human judgment.
What role does reasoning play in expert systems?
In expert systems, reasoning applies stored rules and facts to diagnose problems or provide recommendations in specialized domains.
Can reasoning improve decision-making in dynamic environments?
Yes. Reasoning helps AI adapt quickly to new data, ensuring better decisions in fast-changing real-world scenarios like traffic, finance, or healthcare.
How is reasoning different from learning in AI?
Learning focuses on finding patterns from data, while reasoning applies logic to existing knowledge to reach conclusions or solve problems.
Sources:
- IBM Research – Artificial Intelligence Research
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy – Logic and Artificial Intelligence
- MIT News – Advances in Artificial Intelligence

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks