What Is Cybersecurity? Definition, Types, and How It Works
Published: 6 Jan 2026
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting digital systems, networks, and data from cyber threats such as malware, ransomware, phishing scams, and unauthorized access. It combines technologies, processes, and policies designed to prevent cyberattacks, safeguard sensitive information, and maintain the integrity of information technology systems across organizations and individuals.
As cloud computing, remote work, Internet of Things devices, and artificial intelligence applications continue to expand, the digital attack surface has grown significantly. Cybersecurity addresses these risks through risk management strategies, threat detection, vulnerability management, and incident response, helping organizations reduce data breaches, financial loss, and operational disruption.
In modern environments, cybersecurity is not limited to technical defenses alone. It also includes security awareness, access control, identity protection, and compliance with recognized cybersecurity frameworks such as those developed by national and international standards bodies. Understanding what cybersecurity is and how it works is essential for protecting digital assets, supporting business continuity, and maintaining trust in an increasingly connected world.
Table of Contents
Types of Cybersecurity
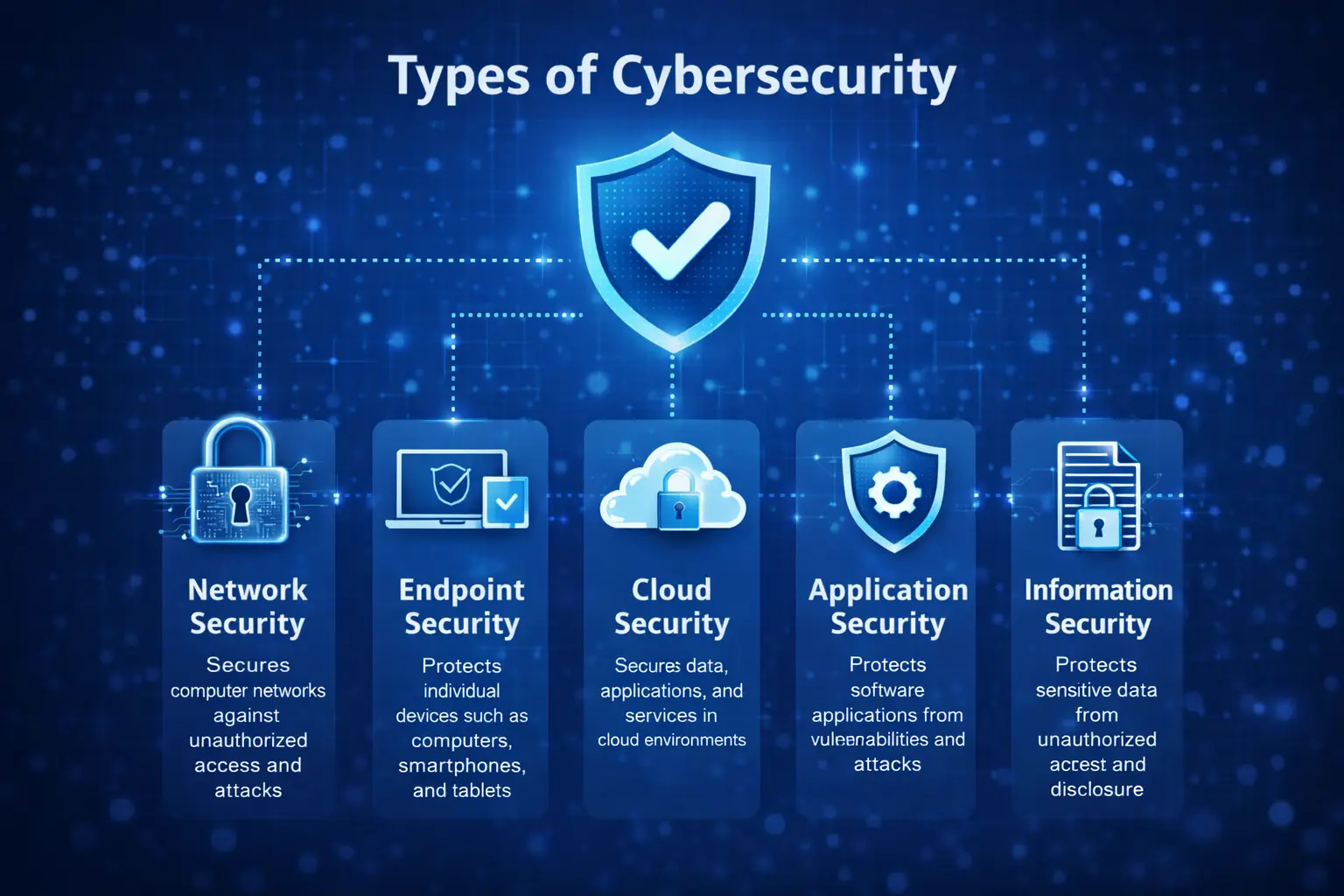
Cybersecurity is not a single layer of protection. It is a combination of specialized security domains designed to protect different parts of digital infrastructure. Each type of cybersecurity focuses on specific systems, data flows, and threat surfaces that exist within modern technology environments.
Network security protects internal networks from unauthorized access, malicious traffic, and intrusion attempts by using controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and traffic monitoring. Endpoint security focuses on securing individual devices such as laptops, mobile phones, and servers, which are common entry points for malware and phishing attacks. Application security addresses vulnerabilities in software and web applications by securing code, APIs, and authentication mechanisms.
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud platforms, cloud security has become a critical area that protects data, workloads, and services hosted in cloud environments. Information security focuses on safeguarding sensitive data through encryption, access control, and data protection policies, regardless of where the data is stored or processed. In connected environments, IoT security ensures that smart devices and sensors do not become weak points within larger systems.
Together, these types of cybersecurity form a layered defense model that helps organizations reduce risk, protect digital assets, and maintain a strong security posture across evolving technology landscapes.
How Cybersecurity Works
How cybersecurity works can be understood by examining how potential risks to digital systems are identified, protective controls are applied, and suspicious activity is continuously monitored. Instead of relying on a single defense, modern cybersecurity uses a layered approach that combines prevention, detection, and response to reduce the impact of cyber threats.
The process begins with risk assessment, where organizations evaluate their information technology infrastructure to identify vulnerabilities, sensitive data, and potential attack paths. Based on this assessment, security measures such as access control, encryption, network monitoring, and endpoint protection are implemented to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. These controls help reduce exposure across networks, devices, applications, and cloud environments.
Once protective measures are in place, cybersecurity relies on threat detection and monitoring to identify malicious activity in real time. Security systems analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to detect anomalies that may indicate cyberattacks such as malware infections, phishing attempts, or insider threats. When a security incident is detected, incident response procedures are activated to contain the threat, minimize damage, and restore normal operations.
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process rather than a one time setup. As technologies evolve and new threats emerge, organizations continuously update their security posture through vulnerability management, security awareness training, and alignment with recognized cybersecurity frameworks. This adaptive approach ensures that digital systems remain resilient against both known and emerging cyber risks.
Why Cybersecurity Is Important
Cybersecurity is essential because digital systems now support critical functions across businesses, governments, and everyday life. From financial transactions and healthcare records to communication platforms and industrial operations, modern society depends on the availability, integrity, and confidentiality of digital information. Without effective cybersecurity, these systems become vulnerable to disruption, data loss, and misuse.
Cyber threats can cause significant consequences beyond technical damage. Data breaches often lead to financial losses, legal penalties, reputational harm, and loss of customer trust. For individuals, cybersecurity failures can result in identity theft, privacy violations, and financial fraud. For organizations, even a single security incident can interrupt operations, expose sensitive information, and weaken long term resilience.
As technology environments grow more complex through cloud adoption, remote work, and connected devices, the potential impact of cyberattacks increases. Cybersecurity helps manage these risks by protecting digital assets, supporting regulatory compliance, and ensuring that systems can continue operating safely in the presence of evolving threats. In this way, cybersecurity is not only a technical requirement but also a foundational element of business continuity, public safety, and digital trust.
Common Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats refer to malicious activities that attempt to compromise digital systems, steal data, or disrupt normal operations. These threats exploit technical vulnerabilities, human behavior, and misconfigured systems to gain unauthorized access or cause harm. As digital environments expand, the variety and sophistication of cyber threats continue to increase.
One of the most common threats is malware, which includes malicious software designed to damage systems, steal information, or gain persistent access. Malware can enter systems through infected files, compromised websites, or unsafe downloads. Ransomware is a specific type of malware that encrypts data and demands payment for its release, often causing severe operational disruption for organizations.
Phishing attacks target users rather than systems by using deceptive messages to trick individuals into sharing sensitive information such as login credentials or financial data. These attacks often appear as legitimate emails, messages, or websites, making them difficult to detect without proper awareness. In addition to external threats, insider threats can arise when authorized users misuse access intentionally or accidentally, leading to data exposure or system compromise.
Cyber threats are not limited to software based attacks. Weak passwords, unpatched systems, misconfigured cloud services, and insecure connected devices can all increase exposure to attacks. Understanding common cybersecurity threats helps organizations and individuals recognize risks early and apply appropriate security measures to reduce the likelihood and impact of incidents.
Cybersecurity Frameworks and Best Practices
Cybersecurity frameworks provide structured guidance for managing security risks and building consistent protection across digital environments. These frameworks define common principles, processes, and controls that help organizations assess their security posture, identify gaps, and improve resilience against cyber threats. Rather than focusing on specific tools, frameworks emphasize repeatable and measurable security practices.
Most cybersecurity frameworks are built around core functions such as risk identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery. By following these functions, organizations can align their security efforts with business objectives while maintaining compliance with regulatory and industry requirements. Framework based approaches also support clearer communication between technical teams, management, and external stakeholders.
Best practices in cybersecurity focus on applying these framework principles in day to day operations. This includes implementing strong access controls, keeping systems updated through regular patching, encrypting sensitive data, monitoring activity for anomalies, and training users to recognize security risks. Security awareness plays a critical role, as human error remains one of the most common causes of security incidents.
Cybersecurity frameworks and best practices are not static. As technologies evolve and new threats emerge, organizations must continuously review and adapt their security strategies. Regular assessments, incident reviews, and process improvements help ensure that cybersecurity efforts remain effective over time and aligned with changing digital environments.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity plays a fundamental role in protecting digital systems, data, and operations in an increasingly connected world. As organizations and individuals rely more heavily on cloud computing, remote access, and interconnected devices, the need for effective cybersecurity becomes essential to maintaining trust, stability, and continuity.
Understanding what cybersecurity is, the different types of cybersecurity, and how cybersecurity works provides a strong foundation for recognizing risks and applying appropriate protections. From preventing cyber threats and securing sensitive information to supporting regulatory compliance and business resilience, cybersecurity functions as an ongoing process rather than a one time solution.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, a structured and adaptive approach to cybersecurity helps ensure that digital environments remain secure over time. By combining technical controls, risk management strategies, and informed human behavior, cybersecurity enables safer use of technology and supports the long term reliability of digital systems across industries and everyday life.
FAQs
What is cybersecurity in simple words?
Cybersecurity means protecting computers, networks, and data from digital threats such as hacking, malware, and unauthorized access. It focuses on keeping information safe and ensuring that digital systems work properly without being disrupted or misused.
What are the 5 types of cybersecurity?
The five main types of cybersecurity are network security, endpoint security, application security, cloud security, and information security. Each type focuses on protecting a specific part of digital infrastructure and works together to reduce overall cyber risk.
How does cybersecurity protect data?
Cybersecurity protects data by using security measures such as encryption, access control, monitoring systems, and secure authentication methods. These measures help prevent unauthorized access, detect suspicious activity, and reduce the risk of data breaches.
What are the biggest cybersecurity threats today?
Some of the most common cybersecurity threats include malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and social engineering. Weak passwords, unpatched systems, and insecure cloud configurations also increase the risk of cyber incidents.
Why is cybersecurity important for individuals and businesses?
Cybersecurity is important because it helps protect personal information, financial data, and critical systems from theft, fraud, and disruption. For businesses, strong cybersecurity supports operational continuity, regulatory compliance, and long term trust with customers and partners.
Is cybersecurity one word or two?
Cybersecurity is commonly written as one word in modern usage. While “cyber security” was used more frequently in the past, most organizations, standards bodies, and publications now use “cybersecurity” as a single word.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





