Why Do the Internet of Things and Smart Homes Matter?
Published: 13 Dec 2025
Houses connected via the Internet of Things (IoT) allow for automated control of household applications, thereby adding efficiencies in terms of comfort, safety, and energy usage.
IoT uses environmental sensors to collect data, device controllers to activate actions based on this data, and communication hubs to unify the operation of various devices from different areas within the home. A smart home incorporates all of these IoT advancements to control light, heat, security, appliance operation, and energy consumption based upon predictable characteristics of the devices within it. Connected thermostats can reduce heating costs, and automated lighting systems can prevent unnecessary electricity usage. Consumers purchase IoT products to help them create energy-efficient routines, gain remote access, and maintain consistency in monitoring their homes. New protocols such as Matter and Zigbee will spur the growth of IoT products by enabling more devices from diverse manufacturers to work with each other.
Table of Contents
This article discusses the operation of an iot system, the technologies that enable automation of home applications, the benefits and drawbacks that drive consumer purchasing behaviour, and how future developments will impact residential living environments.
What Is the Relationship Between the Internet of Things and Smart Homes?
The Internet of Things is connecting connected devices in homes and automating daily tasks using these connected devices in smart homes.

Motion, temperature, air quality, and energy consumption are all monitored in real-time by IoT sensors. Hubs receive these signals from the sensors and provide communication between the different connected devices via protocols such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, or Matter. The automation engine interprets events as they occur and creates automated routines that trigger smart lighting and other connected devices to behave as expected (for example, turning on or off at a certain time at the appropriate temperature).
Key triples
- Sensor → sends → motion or temperature data
- Hub → coordinates → device responses
- Automation engine → activates → routines and scenes
This relationship improves efficiency, increases security, and supports consistent energy control across the home.
How Does the Internet of Things and Smart Home Technology Work?
The Internet of Things (IoT) technology, used in smart homes, uses the connectivity of various devices to create a communication network between the different types of devices by utilizing wireless protocols.
Sensors gather data about movement, temperature and air quality, among other things. The devices will communicate with the hub through wireless protocols like Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi 6, and Matter to establish and keep an ongoing connection with the hub. Automated systems analyse these events and trigger routines that allow for the control of lighting, heating and cooling systems, security systems, and home appliances.
Core technologies
| Technology | Predicate | Object |
| Zigbee | links | low-power sensors |
| Z-Wave | builds | mesh networks |
| Wi-Fi 6 | increases | throughput |
| Matter | unifies | cross-brand devices |
| MQTT | manages | lightweight messages |
| Edge-AI | processes | local events |
These technologies create reliable data flows, reduce delays, and support real-time automation across the home.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Smart Homes With IoT?
IoT smart home systems (Internet of Things) offer improved efficiency and automation while creating potential problems with privacy, reliability and product compatibility issues.
Device energy efficiency will reduce overall energy consumption; security monitoring solutions increase security and Automation solutions relieve consumers of routine tasks. The overall benefit of these devices are only realised if there is a reliable connection between the devices, proper firmware is installed on all devices, and all device data is managed securely.
Advantages
- Thermostats reduce energy use by 10–15 per cent
- Smart lighting cuts electricity consumption by 20–30 per cent
- Cameras and sensors improve security coverage
- Automation engines reduce manual actions and routine tasks
Disadvantages
- Data leaks increase privacy risks
- Device ecosystems create compatibility issues
- Firmware updates require ongoing attention
- Network outages interrupt automation processes
These factors influence how users assess the value and reliability of connected home systems.
What Challenges and Solutions Exist for IoT in Smart Homes?
The security, interoperability, and performance issues associated with iot smart homes can be resolved by implementing stronger standards and more robust processing models.
Device security concerns are associated with the use of weak authentication methods or the use of older versions of firmware. Interoperability issues occur when brands do not have compatible protocols or closed ecosystems. Performance limitations are present when network congestion occurs due to large amounts of data being transferred, or there are moments of latency due to peaks in activity.
Challenge → Solution
- Weak authentication → strong encryption
- Fragmented protocols → Matter standard
- Network latency → edge processing
- Vulnerable firmware → automatic updates
These solutions stabilise device behaviour, strengthen security, and improve automation reliability in connected homes.
What Should an Internet of Things and Smart Home Infographic Show?
An infographic illustrating a smart home IoT ecosystem provides insight into device communication and data transfer within a platform, along with automation’s response to various triggers.
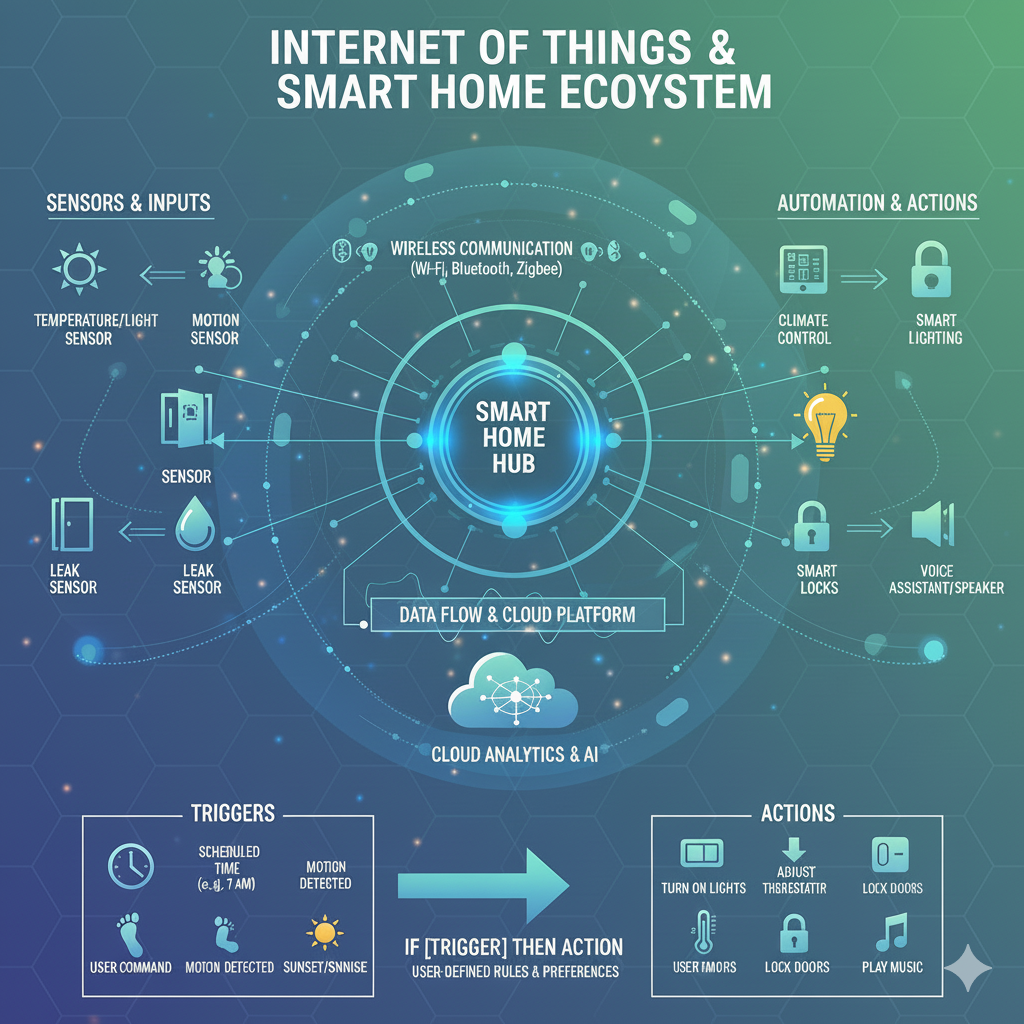
This infographic also illustrates key component locations, including the use of sensors, the hub as a central coordinator, and communication methods that utilise wireless technologies to facilitate the use of automation via triggers and actions based on the user’s defined schedule or preferences. Additionally, the infographic contains lots of graphics that visually differentiate between these components and create the impression that they are all part of a cohesive automation network.
Typical elements
- Sensor clusters that track temperature, motion, or air quality
- Central hub with supported protocol icons
- Arrows that illustrate data flow paths
- Trigger–condition–action logic for automation routines
These elements help readers visualize how IoT and smart home systems work together.
What Are the Key Internet of Things Smart Home Devices and Controllers?
IoT smart home systems utilize a combination of sensors, actuators, hubs, and controllers to automate function within a home.
The sensors capture live environmental data and relay this information to the Actuator, where the Actuator carries out actions on physical objects. The Hubs facilitate communication using Matter, Zigbee, and/or Z-Wave and/or Wi-Fi protocols. The Controllers execute Routines and coordinate the Actions of connected devices using various Applications and/or Voice Assistants.
Devices
- The thermostat regulates the indoor temperature
- The leak sensor detects water issues
- Door lock controls access
- Air-quality sensor measures CO₂ and particulate levels
- Light controller adjusts brightness and scenes
Controllers
- Voice assistants process spoken commands
- Multi-protocol hubs connect different device standards
- Mobile dashboards manage automation rules
These components create the functional framework that supports connected home automation.
How Do IoT Standards Improve Smart Home Integration?
The use of IoT standards allows for devices made by diverse manufacturers to communicate reliably, thereby improving interoperability for Smart Homes.
Standards outline the protocols of interactions between Devices, including Data Exchange, Device Authentication, and Synchronizing Automation Routines. Standards like Matter, Thread and others reduce Device Interoperability Fragmentation by enabling the seamless integration of all types of Sensors, Hubs and Controllers into a single unified IoT Ecosystem.
Key triples
- Matter → unifies → multi-brand devices
- Thread → builds → low-power mesh networks
- Standard protocols → improve → automation reliability
These standards simplify installation, reduce compatibility issues, and support long-term device performance.
How Do Users Choose the Best IoT Smart Home Setup?
When evaluating potential IoT smart home setups, users rely on various criteria, including device compatibility, energy efficiency, security features, and long-term manufacturer support.
Creating a reliable IoT smart home system relies on utilising stable communication protocols, having responsive applications, and appropriately automating tasks. To meet customer needs, manufacturers should ensure their products support the Matter protocol, provide secure authentication methods, and define clear processes for upgrading to new versions of their software and hardware products.
Key criteria
- Device compatibility across brands
- Support for Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi 6, or Matter
- Strong encryption and local processing options
- App usability and automation flexibility
- Update frequency and manufacturer reliability
These criteria help users build a stable and scalable connected home.
What Future Trends Shape Internet of Things and Smart Home Technology?
Future versions of smart homes will rely upon predictive automation, energy modelling, and adaptive autonomous routines based on user behaviour.
AI’s ability to learn patterns, anticipate requirements, and adjust its operation automatically eliminates the need for manual activation of systems. Energy-efficient technologies will use real-time data to optimise heating, cooling, and lighting automatically. The increased adoption of Matter will enhance interoperability between devices, regardless of their purpose, allowing for improved integration across various device classes and industries.
Key trends
- Predictive automation that learns routines
- Energy optimisation using real-time consumption data
- Autonomous device coordination with fewer manual inputs
- Wider Matter support across appliances and sensors
- Growth of edge-AI for faster local processing
These trends shape the next generation of connected homes.
Conclusion
By establishing connections between devices, systems, and users through technology like IoT, it has never been easier for anyone to connect all their devices, thereby increasing the level of interconnectedness among devices.
Smart devices collect information about their surroundings, analyse it, and provide intelligent responses. Users benefit from the consistent behaviour of connected devices, especially when they all use the same protocols like Matter. Users will continue to experience the security and benefits provided by the standardisation of communication for their smart devices, including continuous monitoring of the environment to ensure a higher level of security for users.
Energy savings and reduced costs are caused by the use of automated systems, which are built to eliminate human involvement in the operation of those systems. Manufacturers’ ability to expand the functionality of smart devices will increase both the ability of homes to work more independently and the reliability of those homes. The combination of intelligent devices and secure environments, as well as the use of adaptive automation, will lead to the future development of smart living spaces, where a home’s response to user activity can be predicted.
FAQs
What makes IoT critical for building a functional smart home?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an integral part of the entire infrastructure, integrating all devices, from sensors to hubs and controllers. An IoT solution can provide automation for lighting and climate control, security, and appliances by collecting real-time data, coordinating device operation, allowing for remote access, voice control, and multi-room automated controls.
How does a smart home improve energy efficiency through IoT?
Smart Homes utilize sensors and automated systems to reduce and adjust temperature, heating, and lighting based on time, temperature, and occupancy. Devices will maximize energy efficiency by reducing the amount of energy used when not needed (standby), scheduling tasks based on when the device is not busy, and identifying and eliminating other undesired energy usage (unnecessary consumption).
Are IoT smart homes secure, and what risks should users consider?
When connected devices utilise strong encryption, have updated firmware, and utilise authenticated access, smart IoT homes have higher levels of security. Most risks are created from weak passwords, outdated hardware, unencrypted information being transmitted over a network, and poorly secured or configured networks. It is recommended to utilise secure routers and perform frequent updates to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Which wireless protocol is best for IoT smart home devices?
Matter increases cross-brand compatibility. Zigbee has a focus on low-power devices (sensors). Z-Wave focuses on stable mesh networks and Wi-Fi 6 supports high-bandwidth devices. The optimal communication protocol is contingent upon the type of device(s), power requirements and physical configuration of the home(s).
Do IoT smart home devices work during internet outages?
When hubs can process locally, many automations are functional during outages, and local routines react to events related to light, temperature, or security. However, any automations that rely on the Internet or the cloud (including things such as remote access, voice assistant, and cloud back up) will not work until an Internet connection is restored.
How can users secure their IoT smart home?
By encrypting their smart home devices, setting individual passwords, updating firmware frequently, creating unique networks for their IoT devices, disabling unused ports, and selecting secure devices, consumers can protect themselves. Users can also reduce exposure to cloud threats through local processing.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





