Cybersecurity Strategy and Implementation Plan Essentials
Published: 24 Jan 2026
A cybersecurity strategy and implementation plan (CSIP) is a comprehensive framework designed to protect an organization’s digital assets and information from cyber threats. It outlines the goals, objectives, and specific actions needed to establish and maintain a strong security posture. This document will explore what a cybersecurity strategy is, how to develop one, and the key steps involved in its implementation.
A well-defined cybersecurity strategy offers several key benefits. It helps organizations to proactively manage cybersecurity risks, comply with relevant regulations, and protect their reputation and financial stability. By implementing a robust CSIP, businesses can minimize the impact of cyberattacks, ensure business continuity, and maintain customer trust.
The applications of a cybersecurity strategy are broad and encompass all aspects of an organization’s IT infrastructure and data. It guides decisions related to technology investments, security policies, employee training, and incident response. It addresses areas such as network security, endpoint security, data protection, and cloud security.
The main components of a CSIP include risk assessment, security policies, security controls, incident response planning, and ongoing monitoring. These components work together to create a layered defense that protects against a wide range of cyber threats. The 7 Steps to Developing a Cybersecurity Strategy are explored in more depth below.
Table of Contents
What is a Cybersecurity Strategy?
A Cybersecurity Strategy is a high-level plan that outlines an organization’s approach to managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks. It defines the organization’s security goals, objectives, and priorities, and provides a roadmap for achieving them. The strategy should be aligned with the organization’s overall business objectives and risk tolerance. It also needs to consider the current and adaptive threat landscape.
Developing a Cybersecurity Strategy
Developing a Cybersecurity Strategy involves a systematic process of assessing risks, defining objectives, and creating a plan of action. It requires collaboration between IT professionals, business leaders, and other stakeholders to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective. The strategy should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the threat landscape and the organization’s business needs.
How to Develop and Implement a Cybersecurity Strategy
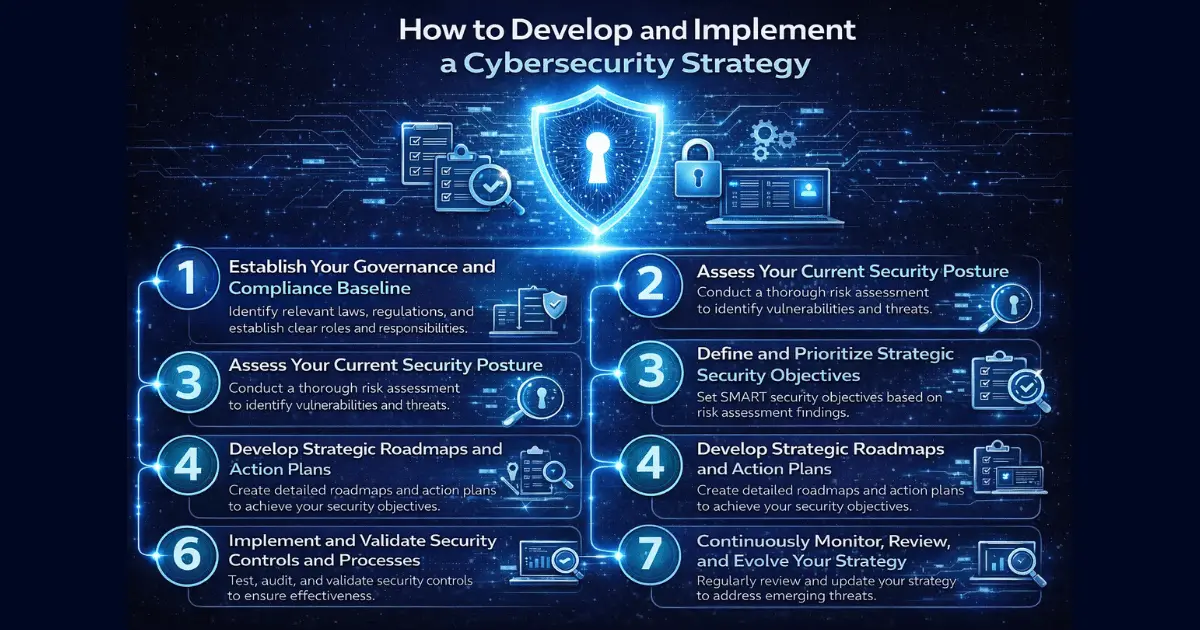
Developing and implementing a cybersecurity strategy is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and execution. The following steps provide a framework for creating a robust and effective CSIP:
Step 1: Establish Your Governance and Compliance Baseline
The first step is to establish a strong governance and compliance baseline. This involves identifying the relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards that apply to your organization. This includes regulations like FISMA. It also involves establishing clear roles and responsibilities for cybersecurity within the organization. A strong governance structure ensures that cybersecurity is treated as a strategic priority and that resources are allocated effectively.
Step 2: Assess Your Current Security Posture
Next, conduct a thorough assessment of your current security posture. This involves identifying your organization’s assets, assessing their vulnerabilities, and evaluating the likelihood and impact of potential cyber threats. A risk assessment should consider all aspects of your IT infrastructure, including networks, systems, applications, and data. Vulnerability Management is key here.
Step 3: Define and Prioritize Strategic Security Objectives
Based on the risk assessment, define and prioritize strategic security objectives. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Examples of strategic security objectives include reducing the number of successful cyberattacks, improving incident response times, and enhancing security awareness among employees. Strategic Security Objectives should align to the overall organization objectives.
Step 4: Develop Strategic Roadmaps and Action Plans
Develop strategic roadmaps and action plans to achieve your security objectives. These roadmaps should outline the specific steps that need to be taken, the resources required, and the timelines for completion. Action plans should assign responsibilities for each task and establish clear metrics for measuring progress. Strategic Roadmaps and Action Plans help ensure accountability and track progress.
Step 5: Select and Integrate Enabling Technologies and Controls
Select and integrate enabling technologies and controls to support your cybersecurity strategy. This may involve implementing new security tools, upgrading existing systems, or modifying security policies and procedures. Enabling Technologies and Controls should be carefully evaluated to ensure that they are effective and compatible with your organization’s IT environment.
Step 6: Implement and Validate Security Controls and Processes
Implement and validate security controls and processes to ensure that they are working as intended. This involves testing security controls, conducting security audits, and performing vulnerability scans. Validate Security Controls regularly to identify and address any weaknesses or gaps in your security posture.
Step 7: Continuously Monitor, Review, and Evolve Your Strategy
Continuously Monitor, Review, and Evolve Your Strategy to adapt to changes in the threat landscape and the organization’s business needs. This involves regularly monitoring security metrics, reviewing incident reports, and updating security policies and procedures. The CSIP should be a living document that is regularly updated to reflect the latest threats and best practices.
Activate Your Cybersecurity Strategy with Automation
To effectively manage the complexities of modern cybersecurity, organizations should leverage automation. Solutions like Swimlane Turbine can automate security tasks, streamline incident response, and improve overall security effectiveness. SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation and Response) platforms allow security teams to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up their time to focus on more strategic initiatives. With automated incident orchestration, organizations can respond to cyber threats faster and more effectively.
Cybersecurity Strategy FAQs
What are the essential components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy?
The essential components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy include:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and evaluating potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
- Security Policies: Establishing clear guidelines and procedures for protecting sensitive information and systems.
- Security Controls: Implementing technical and administrative measures to prevent, detect, and respond to cyberattacks.
- Incident Response Plan: Developing a plan for responding to and recovering from security incidents.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitoring security metrics and systems to detect and respond to threats.
These components should work together to create a layered defense that protects against a wide range of cyber threats.
What is a cybersecurity strategy example?
A cybersecurity strategy example could involve a financial institution implementing multi-factor authentication for all customer accounts, encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit, and conducting regular penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. It could also include implementing a robust incident response plan to quickly contain and mitigate any security breaches.
What is an enterprise cybersecurity strategy?
An enterprise cybersecurity strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines how a large organization will protect its digital assets and information from cyber threats across all departments and business units. It addresses the unique challenges and complexities of managing cybersecurity in a large, distributed environment. This includes addressing challenges of Data Sovereignty Compliance. The enterprise cybersecurity strategy encompasses governance, risk management, compliance, and technology implementation.
Extend Beyond SOAR: Step into the Future with AI Automation
While SOAR platforms have been valuable for automating security tasks, the future of cybersecurity lies in AI Automation. AI-powered security solutions can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and detect threats in real-time. By leveraging AI and machine learning, organizations can improve their threat detection capabilities, automate incident response, and proactively prevent cyberattacks. AI Automation provides a more scalable and effective approach to managing cybersecurity risks.
Conclusion
A well-crafted Cybersecurity Strategy and Implementation Plan (CSIP) is no longer optional – it’s essential for organizations to protect their digital assets and maintain business continuity. By following a structured approach, from establishing governance and assessing risks to implementing controls and continuously monitoring threats, organizations can build a resilient security posture.
The seven-step framework outlined in this blog provides a clear roadmap for developing and executing a CSIP that aligns with business objectives, addresses vulnerabilities, and prepares for evolving cyber threats. Leveraging automation and AI further enhances effectiveness, allowing security teams to respond faster, reduce human error, and focus on strategic initiatives.
Ultimately, a strong cybersecurity strategy not only safeguards data and IT systems but also supports regulatory compliance, protects organizational reputation, and fosters trust with customers and stakeholders. By continuously reviewing and evolving the CSIP, organizations can stay ahead of threats and turn cybersecurity into a strategic advantage rather than a reactive necessity.
Additional Resources
The Swimlane ARMOR Framework
The Swimlane ARMOR Framework is a methodology for developing and implementing a cybersecurity strategy that is aligned with business objectives and risk tolerance. It provides a structured approach to assessing risks, defining objectives, and creating a plan of action.
Cyber Threat Readiness: Should We Sound The Alarms?
Cyber Threat Readiness is a critical aspect of cybersecurity strategy. Organizations should regularly assess their readiness to respond to cyber threats and take steps to improve their preparedness. This includes conducting tabletop exercises, testing incident response plans, and providing security awareness training to employees.
By implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy and leveraging automation and AI, organizations can effectively protect their digital assets and maintain a strong security posture in the face of evolving cyber threats. It’s important to continuously monitor, review, and Evolve Your Strategy to stay ahead of the threat landscape.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





